Street Lighting, GHGs, and Climate Change
What is the GHG footprint of Street Lighting? What is the problem with global warming, and how can Tondo’s Smart Lighting help?
US President Joe Biden has set a goal of halving greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. 185 countries are committed to the 2016 Paris Agreement, which is a global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Global warming is already recognized as one of the most serious risks to human and animal life, and action should be taken. Drought, flood, forest fires, animal extinction, water shortages, and human health are all consequences of urban growth. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is one of the most important actions we can take to improve our quality of life.
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases that capture heat in the atmosphere – most of us know this part).
Natural amounts are good for some things; without them, the temperature on earth would have been -18 degrees celsius. However, since the Industrial Revolution, human activity has resulted in an increase in greenhouse gas emissions, resulting in the earth overheating.
The well-known GHG footprint is a measurement of a product’s, organization’s, or individual’s total greenhouse gas emissions that include carbon dioxide (CO2) but also include methane and nitrous oxide.
The main causes of the growth in GHG footprint are fuel combustion from natural resources or energy generation, industrial agriculture, particularly animal husbandry, waste combustion, and deforestation.
On a personal level, each of us may reduce our carbon footprint by changing our habits, such as driving less, consuming less, and eating less meat. There are many calculators on the internet that allow us to calculate our own personal ecological footprint by answering a series of questions.
At the industrial level, reducing the carbon footprint will include, among other things, energy efficiency, converting to renewable energies and decreasing the waste of raw materials and food.
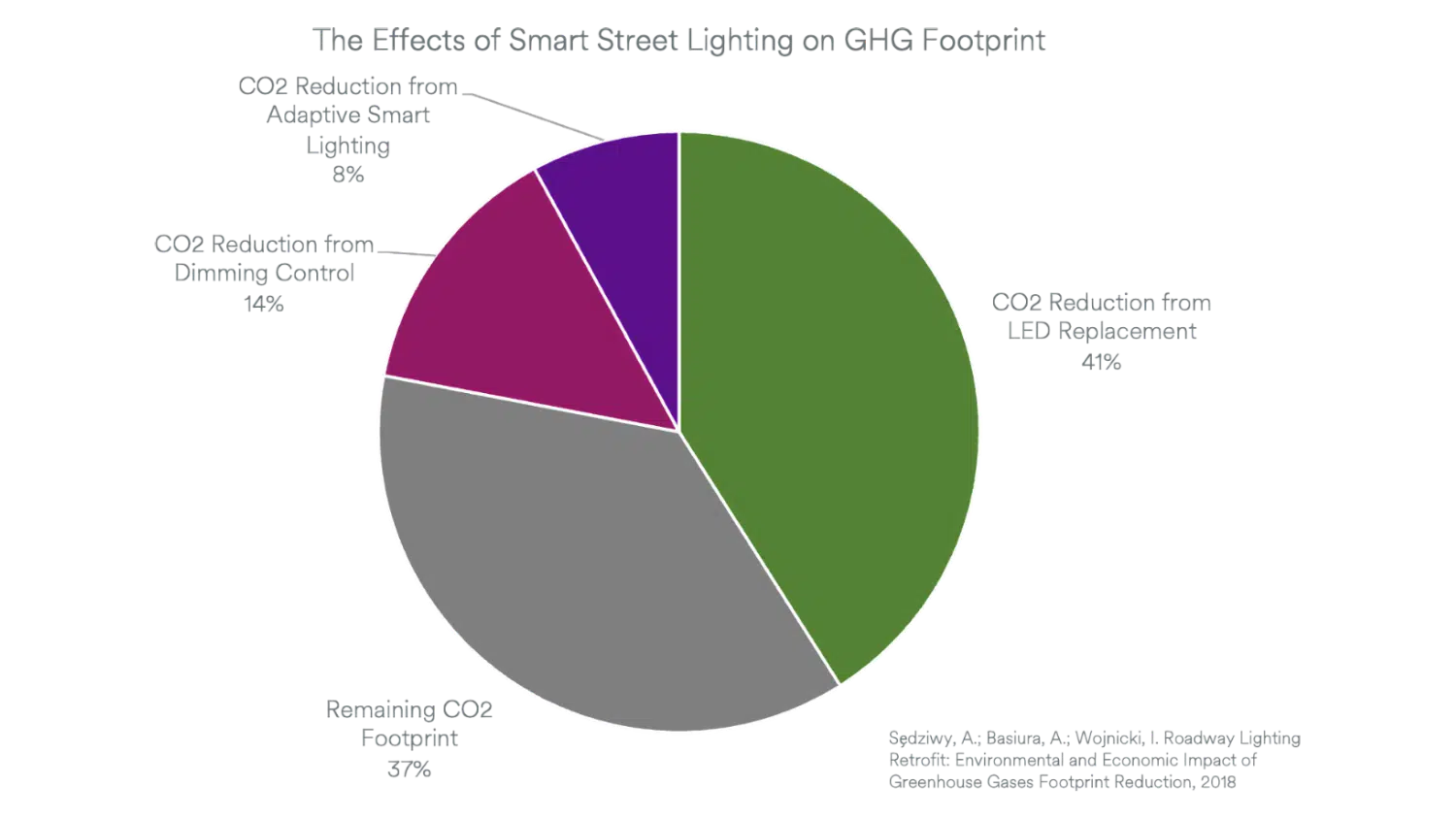
It is estimated that 40% of the carbon footprint comes from electricity generation and 17% from lighting. A 2018 study showed that replacing incandescent lighting with LED lighting resulted in a 41% reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) footprint, followed by a 14% reduction from dimming and an additional 8% reduction in GHG footprint from adaptive smart lighting control. This offers an opportunity for a 22% reduction in the GHG footprint of street lighting using solutions such as Tondo’s Smart Lighting for a combined reduction of 63% in street lighting GHG footprint.
This is the part many people don’t realize: we often take street lighting for granted (except perhaps those of us who work with street lights). We walk through streets, parking lots, and around buildings that are surrounded by lights.
When we stop and think about the fact that wherever there are people, cars, trucks, buildings, sports stadiums, and public transportation, there are outdoor lights.
Most of them are old. They use older, energy-inefficient lamps. They are often controlled in groups rather than individually. When they were originally installed, people didn’t think much of light pollution or energy efficiency.
The electricity they use is produced by a wide range of methods depending on the resources available in their region. It can be clean energy from newer wind, wave, and solar power. However, the majority of electricity generated in the world is generated from burning fossil fuels.
Many organizations are already replacing their outdoor lighting with energy efficient LED lighting, and the savings are significant. With Smart Lighting control, we can take another huge step forward in reducing the massive GHG footprint of outdoor lighting.









0 Comments